Phishing Basics
What is phishing?
Phishing refers to online scams that attempt to trick consumers into revealing personal information, such as check and credit card account numbers, Social Security numbers, or bank account passwords. Most commonly, phishers target unsuspecting users with fake Internet sites or email messages that look startlingly similar to the real thing. This is sometimes referred to as spoofing. Scammers may also leverage social networking sites, where users are already accustomed to sharing information with others.
How does phishing work?
Phishing emails and websites typically use familiar logos and graphics to deceive consumers into thinking the sender or website owner is a government agency, bank, retailer or other company they know or do business with. Sophisticated phishers may include misleading details, such as using the company CEOs name in the email from field. Another common phishing tactic is to make a link in an email (and the fake website where it leads) appear legitimate by subtly misspelling URLs or changing the .com to .biz or another easily overlooked substitution.
Some phishing scams even lure victims by telling them that their information has already been jeopardized. For example, potential victims may receive an email that appears to come from a major bank warning that their account has recently been exposed to fraudulent activity. Users are asked to click a link within the message so they can confirm their bank account information. Instead of going to the banks legitimate website, however, victims are taken to a clever lookalike, where their information actually is routed to identity thieves.
 |
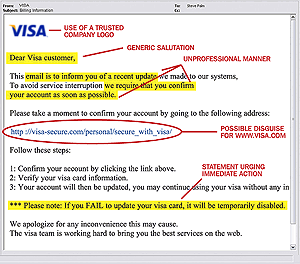 |
If you receive any message asking you to confirm account information that has been stolen or lost or encouraging you to reveal personal information in order to receive a prize, its most likely a form of phishing. In addition to seeking bank information, phishers may also try to obtain your ATM PIN or any other bits of data that can help them build a more complete profile from which they can operate in your name. Never share your personnel information through an email.